Without an established, monitored, and implemented control system and strategy, it is difficult to maintain a level of cloud security compliance that, in some cases, is required by law and regulation. Organisations have a responsibility to their employees, customers, and partners to ensure that cloud resources are consumed responsibly and in line with regulatory requirements.
In this blog, we’ll look at common challenges you may face around cloud compliance and best practices for achieving it.
What is Cloud Security Compliance?
Cloud security compliance refers to the adherence to controls, standards, policies and procedures within an organisation for the goal of achieving better security posture for the cloud environment.
Many organisations will adopt standardised regulatory definitions of cloud security compliance, such as GDPR or Data Protection Act 2018, with the aim of achieving the goals and objectives set out within these regulations. GDPR and Data Protection Act 2018 are both examples of regulations stipulated by law, but there are other regulations you may need to comply with if your organisation works within specific sectors, regions, or otherwise needs to hold itself to a higher standard of cloud security. They could include stipulations on how long data is retained for, the level of encryption required for certain types of information and even the security clearance level of administrators of data held by the business.
Organisations that operate across different regions may also have to consider several jurisdictions and, as such, have to comply with a hybridised version which is compliant with multiple regulatory bodies.
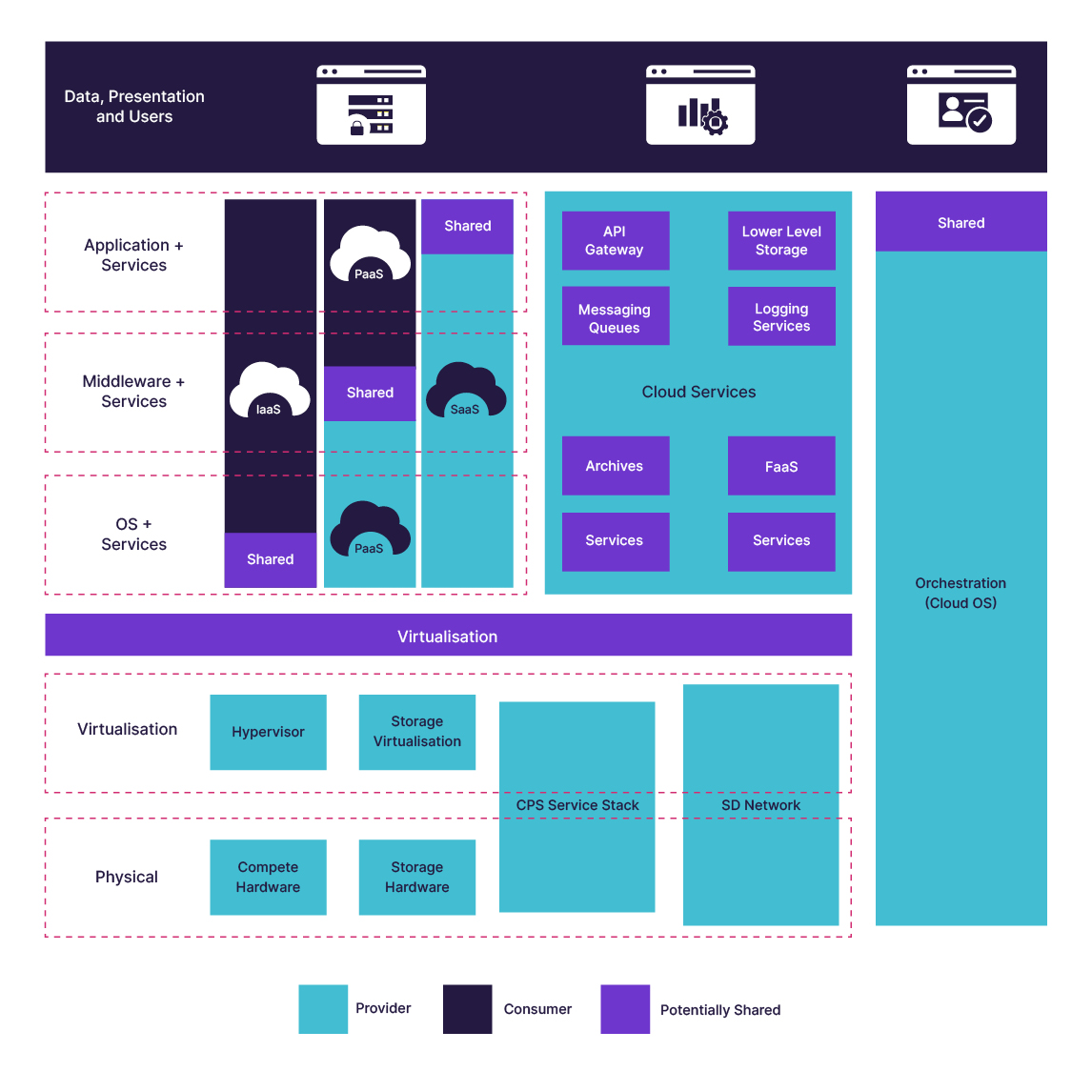
The Shared Responsibility Model for Cloud Security and Compliance
When considering Software as a Service (SaaS) applications, for example, the vast majority of responsibility will be held by the CSP with the customer only being responsible for data, presentation and users. This is in stark contrast to Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), where the customer is responsible for the operating system, service and above, with the CSP generally only being responsible for virtualisation and physical hardware.
Challenges of Cloud Compliance
Some of the challenges facing cloud compliance directly relate to the benefits of adopting cloud infrastructure and practices. Data residence is a significant challenge due to the transient nature of the modern workforce and the availability and elasticity of cloud services.
Many geographical locations have certain regulations and standards which information and data are held to. This can change depending on the location(s) that your business operates in and is made increasingly difficult to manage when your organisation operates in multiple locations.
This is exacerbated by the innate ability of cloud solutions to scale outwards and host information all over the world. As a result, it is imperative that you have a defined policy and process for managing, administering and retaining data and information. This is expensive to incorporate in day-to-day operations and increases the need for dedicated, technical resources.
Cloud Security Compliance Best Practices
Adhering to current best practices is essential to achieving and maintaining compliance. Many CSPs have documentation outlining their recommendations when it comes to securing information and data. Below are just some of the ways you can improve your security posture by achieving cloud security compliance:
Assess the Risk of Information Stored in the Cloud
You must have a robust process in place for assigning risk management and mitigations to data, and ensure that what is hosted is handled appropriately. In essence, you must know what the outcome is if data hosted is mishandled, lost or manipulated and how this effects the individual, the business and the parties involved.
Develop Policies for Sharing Information to the Cloud
To ensure the safety of this information, it’s vital that you develop clear and concise policies for sharing information. These policies must be embedded in the culture of the business, which can take the form of processes and procedures that are delivered through training and technical controls such as Data Loss Prevention (DLP), sensitivity labelling, and encryption in transit.
Review Cloud Service Provider’s Security Policies and Procedures
Due to the shared responsibility of security when leveraging cloud services and solutions, you must ensure that you understands the policies and procedures of the hosting platform. A clear delineation of responsibility must be understood to prevent gaps developing in the security strategy of the organisation.
Backup and Encrypt Your Data
There are many solutions available for the majority of cloud platforms, especially the main three: Azure, AWS and GCP. The use of native solutions and third party tools can mitigate the burden of administration by providing monitoring, automation and management of backups and encryption at rest.
Continuous Compliance Monitoring
Vendor Management
As such, it is the responsibility of the hosting organisation to ensure that robust security processes and controls are extended to their vendors and partners. This can help mitigate potential disparities between the hosting organisation and partner, and ensure that your efforts in securing your cloud ecosystem are not undermined.
Data Residency Awareness
As such, it is vital that you know where your data resides, what regulations it has to meet, and where the flow of data presides.
Documentation and Reporting
Robust documentation and reporting systems can assist you in ensuring that the technical controls implemented to provide cloud security compliance are measured and assured. In addition, this training is much easier to offer to employees when the policies and procedures are clearly documented. Organisations should ensure that reporting is effective and timely to ensure that that technical controls are not undermined.





